Contents
2.7.1 Troubleshooting Authentication and Authorisation
The use of unencrypted credentials is one of the most serious authentication security issues found on systems today. There is no excuse for this. Anyone eavesdropping on the network can intercept and view these plain text credentials.
You can encrypt credentials at the application level by replacing protocols that run in cleartext with secure alternatives that use encryption.
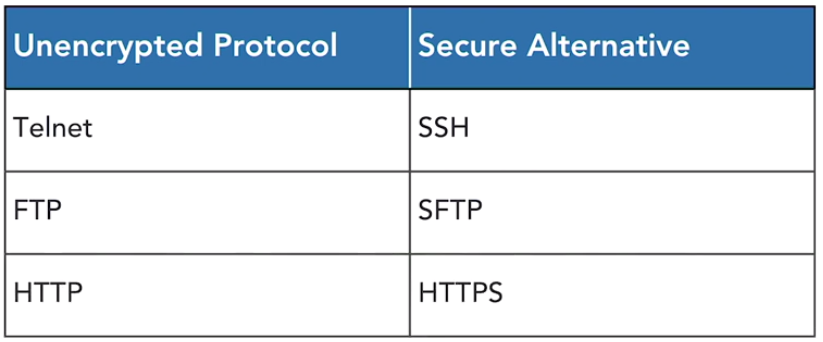
VPNs and SSH Tunnels
IF you are using protocols that don’t have a a secure option, you can add encryption at the network layer by using a VPN or sending traffic through an encrypted SSH tunnel.
Troubleshooting Permission Issues
This can be looking into why a user cant access a certain server, file or network.
Troubleshooting steps:
- Make sure they are using the correct password
- Try using a different account to access the same service. Can that account access it?
- Try accessing a different service with that users account. Maybe there is a problem with the account?
- Investigate authentication logs
Access Violations
These should be thoroughly investigated. Security tools will often report if a user has attempted to exceed their authority. Check the log to see what the user was doing, then reach out to them. It may be a harmless mistake, or they may have been trying to do something they shouldn’t.
2.8.2 Troubleshooting Digital Certificates
Digital certificates are an important security control and are also a source of a wide variety of issues that security professionals wind up troubleshooting.
Certificate Errors
Most people will just click through certificate errors but as a security professional you should investigate them.
NOTE: badssl.com is a website designed purposely with errors to show you the different error messages
- Expired Certificate: this is the most common error. Certificates have an expiration date and if they aren’t renewed in time they expire
- Mismatched Names: this is where the digital certificates name doesn’t match the name of the server. This could be a sign that an error occurred in the server configuration, or that the site is fake and is using the wrong certificate. This is the equivalent of someone trying to prove their identity by using someone else’s drivers licence. The licence is legit, but the picture doesn’t match as it belongs to someone else
- Untrusted CA’s: you should only trust certificates from known and trusted certificate authorities. If you see an error about an untrusted certificate authority you should exercise extreme caution
- Revoked Certificate: If you see this error the site should not be trusted. Certificates may be compromised and the owner of a certificate can revoke them if they lose control. If you see site with an error about the certificate revoked it means the owner or certificate authority believes the certificate was comprised and no longer trusts it
- Cryptography Error: this might be an error where the site says it cant provide a secure connection because it uses an unsupported protocol
2.8.3 Device Configuration Issues
Patch Device Regularly
The single most common security issue with any type of device is the use of outdated firmware or software. Security updates fix crucial issues on devices and applications. Unpatched systems are often defenceless against exploits.
Avoid Weak Cryptography
Things change quickly in the world of cryptography and you should vet any algorithm you plan to use against current security information. You should avoid using the following-
Weak Algorithms:
- Data Encryption Standard (DES)
- Rivest Cipher 4 (RC4)
Weak Hash Functions:
- Message Digest (MD4)
- Message Digest (MD5)
- Secure Ash Algorithm 1 (SHA-1)
The longer the encryption key the more secure the data will be. Make sure the key is appropriate for the situation.
Account Control
Many devices come with default accounts. If you are not using these make sure to disable them or at least change the password.
Troubleshooting Content Filters
Content filters are used to prevent users accessing websites they shouldn’t. Make sure you are filtering the appropriate categories. EG: a financial firm will have different requirements to a school. You will need to manage policy exceptions in cases where a site is mistakenly blocked by a category.
Troubleshooting Wireless Authentication Issues
- Try logging as the user on another system. Are they using the right password?
- Can other users log into the wireless?
- Check the logs
2.8.4 Change and Configuration Management
Information Technology is constantly changing. Change is a good thing, progress comes from change.
Change Management
Organisations must take steps to ensure that change achieves business objectives without disrupting operations. Change management processes ensure that that organisations follow a standardised process for requesting, reviewing, approving, and implementing changes to information systems. The goal is to minimise impact of disruptions to IT services because of change. The standard tool for change management is the “Request for Change” (RFC).
The RFC should include:
- Description of the change
- Expected Impact on the organisation or systems
- Risk assessment
- Rollback plan
- Identity of those involved
- Proposed schedule
- Affected configuration items
Changes must be approved by the relevant authorities.
Baselines
This is an important component of configuration management. A baseline is snapshot of an image at a given point in time. These can be used to assed whether a system has changed outside of an approved change management process. Sys Amins may compare a running configuration to a baseline to identify all the changes and compare those against approved RFC’s.
Software Configuration Management
Tools can be used for the following:
- manage applications and and patches on clients
- detect unauthorised software that is installed on servers or devices
- verify licence compliance
Version Control
This is a critical component n the area of software and script development. Versioning assigns each release of a piece of software an incrementing version number that may be used to identify any given copy. This is generally written as a 3 part decimal. EG: 1.3.1
The first number is the major version of the software
The second number is the major update
The third number is the minor update
2.8.5 Physical Asset Management
Cyber security teams are often responsible for the physical security of technology resources. If a device is lost or stolen it is critical to know what was on that device to perform a security analysis. You need a good inventory process. You cant keep track of your hardware if you don’t know what you have.
Hardware lifecycle:
- User requests new hardware
- Hardware is ordered
- Hardware is received added to inventory and assigned to the user
- Old device is reassigned to another user or properly disposed
- Inventory is updated
Updates to the inventory are critical.
Media Management
Security teams should track media that contains highly sensitive data.
